Caspian Products
- Ampoules
- Anlagesics, Anti-inflammatory Drugs
- Antimyasthenics ,Muscle Relaxants
- Antiparkinson Drugs, Antidepressants,Antiepileptics, Anxiolytic Sedative, Hypnotics and Antipsychotics
- Hormonal Drugs
- Antihistamines, Bronchodilators
- Cardiovascular Drugs,Electrolytes
- Corticosteroids
- General Anaesthetics, Local Anaesthetics
- Antibacterials
- Gastrointestinal Drugs
- Nutritional Agents and Vitamins
- Antagonists
- Suppository
- Syrups & Oral Solutions
- Ointments, Creams & Gels
- Vial
- Prefilled Syringe
Tranexamic Acid
Pharmacology
Tranexamic acid is a competitive inhibitor of plasminogen activation, and at much higher concentrations, a noncompetitive inhibitor of plasmin, i.e., actions similar to aminocaproic acid. Tranexamic acid is about 10 times more potent in vitro than aminocaproic acid.
Tranexamic acid binds more strongly than aminocaproic acid to both the strong and weak receptor sites of the plasminogen molecule in a ratio corresponding to the difference in potency between the compounds. Tranexamic acid in a concentration of 1 mg per mL does not aggregate platelets in vitro.
Tranexamic acid in concentrations up to 10 mg per mL blood has no influence on the platelet count, the coagulation time, or various coagulation factors in whole blood or citrated blood from normal subjects. On the other hand, tranexamic acid in concentrations of 10 mg and 1 mg per mL blood prolongs the thrombin time.
The plasma protein binding of tranexamic acid is about 3% at therapeutic plasma levels and seems to be fully accounted for by its binding to plasminogen. Tranexamic acid does not bind to serum albumin.
After an intravenous dose of 1 g, the plasma concentration time curve shows a triexponential decay with a half-life of about 2 hours for the terminal elimination phase. The initial volume of distribution is about 9 to 12 liters. Urinary excretion is the main route of elimination via glomerular filtration. Overall renal clearance is equal to overall plasma clearance (110 to 116 mL/min), and more than 95% of the dose is excreted in the urine as the unchanged drug. Excretion of tranexamic acid is about 90% at 24 hours after intravenous administration of 10 mg per kg body weight.
An antifibrinolytic concentration of tranexamic acid remains in different tissues for about 17 hours, and in the serum, up to seven or eight hours.
Tranexamic acid passes through the placenta. The concentration in cord blood after an intravenous injection of 10 mg per kg to pregnant women is about 30 mg per liter, as high as in the maternal blood. Tranexamic acid diffuses rapidly into joint fluid and the synovial membrane. In the joint fluid, the same concentration is obtained as in the serum. The biological half-life of tranexamic acid in the joint fluid is about three hours.
The concentration of tranexamic acid in a number of other tissues is lower than in blood. In breast milk, the concentration is about one hundredth of the serum peak concentration. Tranexamic acid concentration in cerebrospinal fluid is about one tenth of that of the plasma. The drug passes into the aqueous humor, the concentration being about one tenth of the plasma concentration.
Tranexamic acid has been detected in semen where it inhibits fibrinolytic activity but does not influence sperm migration.
Pharmacokinetics:
-
Indications:
Tranexamic Acid Injection is indicated in patients with hemophilia for short-term use (two to eight days) to reduce or prevent hemorrhage and reduce the need for replacement therapy during and following tooth extraction.
Contraindications:
1. In patients with acquired defective color vision, since this prohibits measuring one endpoint that should be followed as a measure of toxicity .
2. In patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Anecdotal experience indicates that cerebral edema and cerebral infarction may be caused by Tranexamic Acid Injection in such patients.
3. In patients with active intravascular clotting.
4. In patients with hypersensitivity to tranexamic acid or any of the ingredients
Precautions:
The dose of Tranexamic Acid Injection should be reduced in patients with renal insufficiency because of the risk of accumulation.
Ureteral obstruction due to clot formation in patients with upper urinary tract bleeding has been reported in patients treated with Tranexamic Acid Injection.
Venous and arterial thrombosis or thromboembolism has been reported in patients treated with Tranexamic Acid Injection. In addition, cases of central retinal artery and central retinal vein obstruction have been reported.
Patients with a previous history of thromboembolic disease may be at increased risk for venous or arterial thrombosis.
Tranexamic Acid Injection should not be administered concomitantly with Factor IX Complex concentrates or Anti-inhibitor Coagulant concentrates, as the risk of thrombosis may be increased.
Patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), who require treatment with Tranexamic Acid Injection, must be under strict supervision of a physician experienced in treating this disorder.
Tranexamic acid may cause dizziness and therefore may influence the ability to drive or use machines.
Drug Interactions:
No studies of interaction between tranexamic acid and other drugs have been conducted.
Side Effects:
Back pain; headache; joint pain; muscle pain, spasms, or cramps; nasal or sinus congestion; stomach pain; tiredness.
Severe allergic reactions (rash; hives; itching; difficulty breathing; tightness in the chest or throat; swelling of the mouth, face, lips, or tongue; flushing of the face); calf or leg pain, swelling, or tenderness; chest pain; confusion; coughing up blood; decreased urination or difficulty urinating; eye problems; fainting; numbness of an arm or leg; one-sided weakness; seizures; severe or persistent dizziness or light-headedness; shortness of breath; slurred speech; sudden, severe headache or vomiting; unusual tiredness or weakness; vision changes or problems (eg, disturbance of color vision, sharpness, or field of vision).
Storage:
• Store below 30 C°
• Protect from light and freezing
Packing:
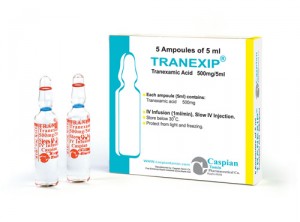
• Injection 500mg/5ml: Box of 5 ampoules

TRANEXIP®
Injection 500mg/5ml
Antifibrinolytic Agent
Haemostatics
Category B
Tranexamic acid is a competitive inhibitor of plasminogen activation, and at much higher concentrations, a noncompetitive inhibitor of plasmin, i.e., actions similar to aminocaproic acid. Tranexamic acid is about 10 times more potent in vitro than aminocaproic acid.
Tranexamic acid binds more strongly than aminocaproic acid to both the strong and weak receptor sites of the plasminogen molecule in a ratio corresponding to the difference in potency between the compounds. Tranexamic acid in a concentration of 1 mg per mL does not aggregate platelets in vitro.
Tranexamic acid in concentrations up to 10 mg per mL blood has no influence on the platelet count, the coagulation time, or various coagulation factors in whole blood or citrated blood from normal subjects. On the other hand, tranexamic acid in concentrations of 10 mg and 1 mg per mL blood prolongs the thrombin time.
The plasma protein binding of tranexamic acid is about 3% at therapeutic plasma levels and seems to be fully accounted for by its binding to plasminogen. Tranexamic acid does not bind to serum albumin.
After an intravenous dose of 1 g, the plasma concentration time curve shows a triexponential decay with a half-life of about 2 hours for the terminal elimination phase. The initial volume of distribution is about 9 to 12 liters. Urinary excretion is the main route of elimination via glomerular filtration. Overall renal clearance is equal to overall plasma clearance (110 to 116 mL/min), and more than 95% of the dose is excreted in the urine as the unchanged drug. Excretion of tranexamic acid is about 90% at 24 hours after intravenous administration of 10 mg per kg body weight.
An antifibrinolytic concentration of tranexamic acid remains in different tissues for about 17 hours, and in the serum, up to seven or eight hours.
Tranexamic acid passes through the placenta. The concentration in cord blood after an intravenous injection of 10 mg per kg to pregnant women is about 30 mg per liter, as high as in the maternal blood. Tranexamic acid diffuses rapidly into joint fluid and the synovial membrane. In the joint fluid, the same concentration is obtained as in the serum. The biological half-life of tranexamic acid in the joint fluid is about three hours.
The concentration of tranexamic acid in a number of other tissues is lower than in blood. In breast milk, the concentration is about one hundredth of the serum peak concentration. Tranexamic acid concentration in cerebrospinal fluid is about one tenth of that of the plasma. The drug passes into the aqueous humor, the concentration being about one tenth of the plasma concentration.
Tranexamic acid has been detected in semen where it inhibits fibrinolytic activity but does not influence sperm migration.
-
Tranexamic Acid Injection is indicated in patients with hemophilia for short-term use (two to eight days) to reduce or prevent hemorrhage and reduce the need for replacement therapy during and following tooth extraction.
1. In patients with acquired defective color vision, since this prohibits measuring one endpoint that should be followed as a measure of toxicity .
2. In patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Anecdotal experience indicates that cerebral edema and cerebral infarction may be caused by Tranexamic Acid Injection in such patients.
3. In patients with active intravascular clotting.
4. In patients with hypersensitivity to tranexamic acid or any of the ingredients
The dose of Tranexamic Acid Injection should be reduced in patients with renal insufficiency because of the risk of accumulation.
Ureteral obstruction due to clot formation in patients with upper urinary tract bleeding has been reported in patients treated with Tranexamic Acid Injection.
Venous and arterial thrombosis or thromboembolism has been reported in patients treated with Tranexamic Acid Injection. In addition, cases of central retinal artery and central retinal vein obstruction have been reported.
Patients with a previous history of thromboembolic disease may be at increased risk for venous or arterial thrombosis.
Tranexamic Acid Injection should not be administered concomitantly with Factor IX Complex concentrates or Anti-inhibitor Coagulant concentrates, as the risk of thrombosis may be increased.
Patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), who require treatment with Tranexamic Acid Injection, must be under strict supervision of a physician experienced in treating this disorder.
Tranexamic acid may cause dizziness and therefore may influence the ability to drive or use machines.
No studies of interaction between tranexamic acid and other drugs have been conducted.
Back pain; headache; joint pain; muscle pain, spasms, or cramps; nasal or sinus congestion; stomach pain; tiredness.
Severe allergic reactions (rash; hives; itching; difficulty breathing; tightness in the chest or throat; swelling of the mouth, face, lips, or tongue; flushing of the face); calf or leg pain, swelling, or tenderness; chest pain; confusion; coughing up blood; decreased urination or difficulty urinating; eye problems; fainting; numbness of an arm or leg; one-sided weakness; seizures; severe or persistent dizziness or light-headedness; shortness of breath; slurred speech; sudden, severe headache or vomiting; unusual tiredness or weakness; vision changes or problems (eg, disturbance of color vision, sharpness, or field of vision).
• Store below 30 C°
• Protect from light and freezing
• Injection 500mg/5ml: Box of 5 ampoules
 )
)
[field_administration_and_dosage] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[value] =>
[format] =>
[safe] =>
[view] =>
)
)
[field_brand_name] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[value] => TRANEXIP®
[format] => 1
[safe] =>
)
)
[field_administration_and_dosage] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[value] =>
[format] =>
[safe] =>
[view] =>
)
)
[field_brand_name] => Array
(
[0] => Array
(
[value] => TRANEXIP®
[format] => 1
[safe] => TRANEXIP®
[view] =>TRANEXIP®
) ) [field_contraindications] => Array ( [0] => Array ( [value] => 1. In patients with acquired defective color vision, since this prohibits measuring one endpoint that should be followed as a measure of toxicity . 2. In patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Anecdotal experience indicates that cerebral edema and cerebral infarction may be caused by Tranexamic Acid Injection in such patients. 3. In patients with active intravascular clotting. 4. In patients with hypersensitivity to tranexamic acid or any of the ingredients [format] => 1 [safe] =>1. In patients with acquired defective color vision, since this prohibits measuring one endpoint that should be followed as a measure of toxicity .
2. In patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Anecdotal experience indicates that cerebral edema and cerebral infarction may be caused by Tranexamic Acid Injection in such patients.
3. In patients with active intravascular clotting.
4. In patients with hypersensitivity to tranexamic acid or any of the ingredients
1. In patients with acquired defective color vision, since this prohibits measuring one endpoint that should be followed as a measure of toxicity .
2. In patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Anecdotal experience indicates that cerebral edema and cerebral infarction may be caused by Tranexamic Acid Injection in such patients.
3. In patients with active intravascular clotting.
4. In patients with hypersensitivity to tranexamic acid or any of the ingredients
Injection 500mg/5ml
[view] =>Injection 500mg/5ml
) ) [field_drug_interactions] => Array ( [0] => Array ( [value] => No studies of interaction between tranexamic acid and other drugs have been conducted. [format] => 1 [safe] =>No studies of interaction between tranexamic acid and other drugs have been conducted.
[view] =>No studies of interaction between tranexamic acid and other drugs have been conducted.
) ) [field_indications] => Array ( [0] => Array ( [value] => Tranexamic Acid Injection is indicated in patients with hemophilia for short-term use (two to eight days) to reduce or prevent hemorrhage and reduce the need for replacement therapy during and following tooth extraction. [format] => 1 [safe] =>Tranexamic Acid Injection is indicated in patients with hemophilia for short-term use (two to eight days) to reduce or prevent hemorrhage and reduce the need for replacement therapy during and following tooth extraction.
[view] =>Tranexamic Acid Injection is indicated in patients with hemophilia for short-term use (two to eight days) to reduce or prevent hemorrhage and reduce the need for replacement therapy during and following tooth extraction.
) ) [field_packing] => Array ( [0] => Array ( [value] => • Injection 500mg/5ml: Box of 5 ampoules [format] => 1 [safe] =>• Injection 500mg/5ml: Box of 5 ampoules
[view] =>• Injection 500mg/5ml: Box of 5 ampoules
) ) [field_pdf] => Array ( [0] => Array ( [fid] => 205 [uid] => 1 [filename] => tranexamic_acid.pdf [filepath] => sites/default/files/pdf/tranexamic_acid.pdf [filemime] => application/pdf [filesize] => 163151 [status] => 1 [timestamp] => 1329493224 [list] => 1 [data] => [i18nsync] => 1 [nid] => 233 [view] => ) ) [field_pharmacokinetics] => Array ( [0] => Array ( [value] => - [format] => 1 [safe] =>-
[view] =>-
) ) [field_pharmacological_category] => Array ( [0] => Array ( [value] => Antifibrinolytic Agent [format] => 1 [safe] =>Antifibrinolytic Agent
[view] =>Antifibrinolytic Agent
) ) [field_precautions] => Array ( [0] => Array ( [value] => The dose of Tranexamic Acid Injection should be reduced in patients with renal insufficiency because of the risk of accumulation. Ureteral obstruction due to clot formation in patients with upper urinary tract bleeding has been reported in patients treated with Tranexamic Acid Injection. Venous and arterial thrombosis or thromboembolism has been reported in patients treated with Tranexamic Acid Injection. In addition, cases of central retinal artery and central retinal vein obstruction have been reported. Patients with a previous history of thromboembolic disease may be at increased risk for venous or arterial thrombosis. Tranexamic Acid Injection should not be administered concomitantly with Factor IX Complex concentrates or Anti-inhibitor Coagulant concentrates, as the risk of thrombosis may be increased. Patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), who require treatment with Tranexamic Acid Injection, must be under strict supervision of a physician experienced in treating this disorder. Tranexamic acid may cause dizziness and therefore may influence the ability to drive or use machines. [format] => 1 [safe] =>The dose of Tranexamic Acid Injection should be reduced in patients with renal insufficiency because of the risk of accumulation.
Ureteral obstruction due to clot formation in patients with upper urinary tract bleeding has been reported in patients treated with Tranexamic Acid Injection.
Venous and arterial thrombosis or thromboembolism has been reported in patients treated with Tranexamic Acid Injection. In addition, cases of central retinal artery and central retinal vein obstruction have been reported.
Patients with a previous history of thromboembolic disease may be at increased risk for venous or arterial thrombosis.
Tranexamic Acid Injection should not be administered concomitantly with Factor IX Complex concentrates or Anti-inhibitor Coagulant concentrates, as the risk of thrombosis may be increased.
Patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), who require treatment with Tranexamic Acid Injection, must be under strict supervision of a physician experienced in treating this disorder.
Tranexamic acid may cause dizziness and therefore may influence the ability to drive or use machines.
The dose of Tranexamic Acid Injection should be reduced in patients with renal insufficiency because of the risk of accumulation.
Ureteral obstruction due to clot formation in patients with upper urinary tract bleeding has been reported in patients treated with Tranexamic Acid Injection.
Venous and arterial thrombosis or thromboembolism has been reported in patients treated with Tranexamic Acid Injection. In addition, cases of central retinal artery and central retinal vein obstruction have been reported.
Patients with a previous history of thromboembolic disease may be at increased risk for venous or arterial thrombosis.
Tranexamic Acid Injection should not be administered concomitantly with Factor IX Complex concentrates or Anti-inhibitor Coagulant concentrates, as the risk of thrombosis may be increased.
Patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), who require treatment with Tranexamic Acid Injection, must be under strict supervision of a physician experienced in treating this disorder.
Tranexamic acid may cause dizziness and therefore may influence the ability to drive or use machines.
Category B
[view] =>Category B
) ) [field_references] => Array ( [0] => Array ( [value] => [format] => [safe] => [view] => ) ) [field_side_effects] => Array ( [0] => Array ( [value] => Back pain; headache; joint pain; muscle pain, spasms, or cramps; nasal or sinus congestion; stomach pain; tiredness. Severe allergic reactions (rash; hives; itching; difficulty breathing; tightness in the chest or throat; swelling of the mouth, face, lips, or tongue; flushing of the face); calf or leg pain, swelling, or tenderness; chest pain; confusion; coughing up blood; decreased urination or difficulty urinating; eye problems; fainting; numbness of an arm or leg; one-sided weakness; seizures; severe or persistent dizziness or light-headedness; shortness of breath; slurred speech; sudden, severe headache or vomiting; unusual tiredness or weakness; vision changes or problems (eg, disturbance of color vision, sharpness, or field of vision). [format] => 1 [safe] =>Back pain; headache; joint pain; muscle pain, spasms, or cramps; nasal or sinus congestion; stomach pain; tiredness.
Severe allergic reactions (rash; hives; itching; difficulty breathing; tightness in the chest or throat; swelling of the mouth, face, lips, or tongue; flushing of the face); calf or leg pain, swelling, or tenderness; chest pain; confusion; coughing up blood; decreased urination or difficulty urinating; eye problems; fainting; numbness of an arm or leg; one-sided weakness; seizures; severe or persistent dizziness or light-headedness; shortness of breath; slurred speech; sudden, severe headache or vomiting; unusual tiredness or weakness; vision changes or problems (eg, disturbance of color vision, sharpness, or field of vision).
Back pain; headache; joint pain; muscle pain, spasms, or cramps; nasal or sinus congestion; stomach pain; tiredness.
Severe allergic reactions (rash; hives; itching; difficulty breathing; tightness in the chest or throat; swelling of the mouth, face, lips, or tongue; flushing of the face); calf or leg pain, swelling, or tenderness; chest pain; confusion; coughing up blood; decreased urination or difficulty urinating; eye problems; fainting; numbness of an arm or leg; one-sided weakness; seizures; severe or persistent dizziness or light-headedness; shortness of breath; slurred speech; sudden, severe headache or vomiting; unusual tiredness or weakness; vision changes or problems (eg, disturbance of color vision, sharpness, or field of vision).
• Store below 30 C°
• Protect from light and freezing
• Store below 30 C°
• Protect from light and freezing
Haemostatics
[view] =>Haemostatics
) ) [field_related_products] => Array ( [0] => Array ( [nid] => [i18nsync] => 1 [safe] => Array ( ) [view] => ) [1] => Array ( [nid] => [i18nsync] => 1 [safe] => Array ( ) [view] => ) [2] => Array ( [nid] => [i18nsync] => 1 [safe] => Array ( ) [view] => ) ) [taxonomy] => Array ( [7] => stdClass Object ( [tid] => 7 [vid] => 1 [name] => Cardiovascular Drugs,Electrolytes [description] => [weight] => 5 [language] => [trid] => 0 [v_weight_unused] => 0 ) ) [build_mode] => 0 [readmore] => 1 [content] => Array ( [field_one_image] => Array ( [#type_name] => product [#context] => full [#field_name] => field_one_image [#post_render] => Array ( [0] => content_field_wrapper_post_render ) [#weight] => -3 [field] => Array ( [#description] => [items] => Array ( [0] => Array ( [#formatter] => image_plain [#node] => stdClass Object *RECURSION* [#type_name] => product [#field_name] => field_one_image [#weight] => 0 [#theme] => imagefield_formatter_image_plain [#item] => Array ( [fid] => 204 [uid] => 1 [filename] => tranexamic_acid_s.jpg [filepath] => sites/default/files/images/tranexamic_acid_s.jpg [filemime] => image/jpeg [filesize] => 65352 [status] => 1 [timestamp] => 1329493113 [list] => 1 [data] => Array ( [alt] => [title] => ) [i18nsync] => 1 [nid] => 233 [#delta] => 0 ) [#title] => [#description] => [#theme_used] => 1 [#printed] => 1 [#type] => [#value] => [#prefix] => [#suffix] => [#children] => )
[#title] =>
[#description] =>
[#children] =>
)
[#title] =>
[#description] =>
[#children] =>  [#printed] => 1
)
[#single] => 1
[#attributes] => Array
(
)
[#required] =>
[#parents] => Array
(
)
[#tree] =>
[#context] => full
[#page] => 1
[#field_name] => field_one_image
[#title] => Image
[#access] => 1
[#label_display] => above
[#teaser] =>
[#node] => stdClass Object
*RECURSION*
[#type] => content_field
[#children] =>
[#printed] => 1
)
[#single] => 1
[#attributes] => Array
(
)
[#required] =>
[#parents] => Array
(
)
[#tree] =>
[#context] => full
[#page] => 1
[#field_name] => field_one_image
[#title] => Image
[#access] => 1
[#label_display] => above
[#teaser] =>
[#node] => stdClass Object
*RECURSION*
[#type] => content_field
[#children] =>  [#printed] => 1
)
[#title] =>
[#description] =>
[#children] =>
[#printed] => 1
)
[#title] =>
[#description] =>
[#children] => 
TRANEXIP®
[#delta] => 0 ) [#title] => [#description] => [#theme_used] => 1 [#printed] => 1 [#type] => [#value] => [#prefix] => [#suffix] => [#children] =>TRANEXIP®
) [#title] => [#description] => [#children] =>TRANEXIP®
[#printed] => 1 ) [#single] => 1 [#attributes] => Array ( ) [#required] => [#parents] => Array ( ) [#tree] => [#context] => full [#page] => 1 [#field_name] => field_brand_name [#title] => Brand Name [#access] => 1 [#label_display] => above [#teaser] => [#node] => stdClass Object *RECURSION* [#type] => content_field [#children] =>TRANEXIP®
[#printed] => 1 ) [#title] => [#description] => [#children] =>TRANEXIP®
Injection 500mg/5ml
[#delta] => 0 ) [#title] => [#description] => [#theme_used] => 1 [#printed] => 1 [#type] => [#value] => [#prefix] => [#suffix] => [#children] =>Injection 500mg/5ml
) [#title] => [#description] => [#children] =>Injection 500mg/5ml
[#printed] => 1 ) [#single] => 1 [#attributes] => Array ( ) [#required] => [#parents] => Array ( ) [#tree] => [#context] => full [#page] => 1 [#field_name] => field_dosage_form [#title] => Dosage Form [#access] => 1 [#label_display] => above [#teaser] => [#node] => stdClass Object *RECURSION* [#type] => content_field [#children] =>Injection 500mg/5ml
[#printed] => 1 ) [#title] => [#description] => [#children] =>Injection 500mg/5ml
Antifibrinolytic Agent
[#delta] => 0 ) [#title] => [#description] => [#theme_used] => 1 [#printed] => 1 [#type] => [#value] => [#prefix] => [#suffix] => [#children] =>Antifibrinolytic Agent
) [#title] => [#description] => [#children] =>Antifibrinolytic Agent
[#printed] => 1 ) [#single] => 1 [#attributes] => Array ( ) [#required] => [#parents] => Array ( ) [#tree] => [#context] => full [#page] => 1 [#field_name] => field_pharmacological_category [#title] => Pharmacological Category [#access] => 1 [#label_display] => above [#teaser] => [#node] => stdClass Object *RECURSION* [#type] => content_field [#children] =>Antifibrinolytic Agent
[#printed] => 1 ) [#title] => [#description] => [#children] =>Antifibrinolytic Agent
Haemostatics
[#delta] => 0 ) [#title] => [#description] => [#theme_used] => 1 [#printed] => 1 [#type] => [#value] => [#prefix] => [#suffix] => [#children] =>Haemostatics
) [#title] => [#description] => [#children] =>Haemostatics
[#printed] => 1 ) [#single] => 1 [#attributes] => Array ( ) [#required] => [#parents] => Array ( ) [#tree] => [#context] => full [#page] => 1 [#field_name] => field_therapeutic_category [#title] => Therapeutic Category [#access] => 1 [#label_display] => above [#teaser] => [#node] => stdClass Object *RECURSION* [#type] => content_field [#children] =>Haemostatics
[#printed] => 1 ) [#title] => [#description] => [#children] =>Haemostatics
Category B
[#delta] => 0 ) [#title] => [#description] => [#theme_used] => 1 [#printed] => 1 [#type] => [#value] => [#prefix] => [#suffix] => [#children] =>Category B
) [#title] => [#description] => [#children] =>Category B
[#printed] => 1 ) [#single] => 1 [#attributes] => Array ( ) [#required] => [#parents] => Array ( ) [#tree] => [#context] => full [#page] => 1 [#field_name] => field_pregnancy_category [#title] => Pregnancy Category [#access] => 1 [#label_display] => above [#teaser] => [#node] => stdClass Object *RECURSION* [#type] => content_field [#children] =>Category B
[#printed] => 1 ) [#title] => [#description] => [#children] =>Category B
Tranexamic acid is a competitive inhibitor of plasminogen activation, and at much higher concentrations, a noncompetitive inhibitor of plasmin, i.e., actions similar to aminocaproic acid. Tranexamic acid is about 10 times more potent in vitro than aminocaproic acid.
Tranexamic acid binds more strongly than aminocaproic acid to both the strong and weak receptor sites of the plasminogen molecule in a ratio corresponding to the difference in potency between the compounds. Tranexamic acid in a concentration of 1 mg per mL does not aggregate platelets in vitro.
Tranexamic acid in concentrations up to 10 mg per mL blood has no influence on the platelet count, the coagulation time, or various coagulation factors in whole blood or citrated blood from normal subjects. On the other hand, tranexamic acid in concentrations of 10 mg and 1 mg per mL blood prolongs the thrombin time.
The plasma protein binding of tranexamic acid is about 3% at therapeutic plasma levels and seems to be fully accounted for by its binding to plasminogen. Tranexamic acid does not bind to serum albumin.
After an intravenous dose of 1 g, the plasma concentration time curve shows a triexponential decay with a half-life of about 2 hours for the terminal elimination phase. The initial volume of distribution is about 9 to 12 liters. Urinary excretion is the main route of elimination via glomerular filtration. Overall renal clearance is equal to overall plasma clearance (110 to 116 mL/min), and more than 95% of the dose is excreted in the urine as the unchanged drug. Excretion of tranexamic acid is about 90% at 24 hours after intravenous administration of 10 mg per kg body weight.
An antifibrinolytic concentration of tranexamic acid remains in different tissues for about 17 hours, and in the serum, up to seven or eight hours.
Tranexamic acid passes through the placenta. The concentration in cord blood after an intravenous injection of 10 mg per kg to pregnant women is about 30 mg per liter, as high as in the maternal blood. Tranexamic acid diffuses rapidly into joint fluid and the synovial membrane. In the joint fluid, the same concentration is obtained as in the serum. The biological half-life of tranexamic acid in the joint fluid is about three hours.
The concentration of tranexamic acid in a number of other tissues is lower than in blood. In breast milk, the concentration is about one hundredth of the serum peak concentration. Tranexamic acid concentration in cerebrospinal fluid is about one tenth of that of the plasma. The drug passes into the aqueous humor, the concentration being about one tenth of the plasma concentration.
Tranexamic acid has been detected in semen where it inhibits fibrinolytic activity but does not influence sperm migration.
[#title] => [#description] => [#printed] => 1 ) [field_pharmacokinetics] => Array ( [#type_name] => product [#context] => full [#field_name] => field_pharmacokinetics [#post_render] => Array ( [0] => content_field_wrapper_post_render ) [#weight] => 4 [field] => Array ( [#description] => [items] => Array ( [0] => Array ( [#formatter] => default [#node] => stdClass Object *RECURSION* [#type_name] => product [#field_name] => field_pharmacokinetics [#weight] => 0 [#theme] => text_formatter_default [#item] => Array ( [value] => - [format] => 1 [safe] =>-
[#delta] => 0 ) [#title] => [#description] => [#theme_used] => 1 [#printed] => 1 [#type] => [#value] => [#prefix] => [#suffix] => [#children] =>-
) [#title] => [#description] => [#children] =>-
[#printed] => 1 ) [#single] => 1 [#attributes] => Array ( ) [#required] => [#parents] => Array ( ) [#tree] => [#context] => full [#page] => 1 [#field_name] => field_pharmacokinetics [#title] => Pharmacokinetics [#access] => 1 [#label_display] => above [#teaser] => [#node] => stdClass Object *RECURSION* [#type] => content_field [#children] =>-
[#printed] => 1 ) [#title] => [#description] => [#children] =>-
Tranexamic Acid Injection is indicated in patients with hemophilia for short-term use (two to eight days) to reduce or prevent hemorrhage and reduce the need for replacement therapy during and following tooth extraction.
[#delta] => 0 ) [#title] => [#description] => [#theme_used] => 1 [#printed] => 1 [#type] => [#value] => [#prefix] => [#suffix] => [#children] =>Tranexamic Acid Injection is indicated in patients with hemophilia for short-term use (two to eight days) to reduce or prevent hemorrhage and reduce the need for replacement therapy during and following tooth extraction.
) [#title] => [#description] => [#children] =>Tranexamic Acid Injection is indicated in patients with hemophilia for short-term use (two to eight days) to reduce or prevent hemorrhage and reduce the need for replacement therapy during and following tooth extraction.
[#printed] => 1 ) [#single] => 1 [#attributes] => Array ( ) [#required] => [#parents] => Array ( ) [#tree] => [#context] => full [#page] => 1 [#field_name] => field_indications [#title] => Indications [#access] => 1 [#label_display] => above [#teaser] => [#node] => stdClass Object *RECURSION* [#type] => content_field [#children] =>Tranexamic Acid Injection is indicated in patients with hemophilia for short-term use (two to eight days) to reduce or prevent hemorrhage and reduce the need for replacement therapy during and following tooth extraction.
[#printed] => 1 ) [#title] => [#description] => [#children] =>Tranexamic Acid Injection is indicated in patients with hemophilia for short-term use (two to eight days) to reduce or prevent hemorrhage and reduce the need for replacement therapy during and following tooth extraction.
1. In patients with acquired defective color vision, since this prohibits measuring one endpoint that should be followed as a measure of toxicity .
2. In patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Anecdotal experience indicates that cerebral edema and cerebral infarction may be caused by Tranexamic Acid Injection in such patients.
3. In patients with active intravascular clotting.
4. In patients with hypersensitivity to tranexamic acid or any of the ingredients
1. In patients with acquired defective color vision, since this prohibits measuring one endpoint that should be followed as a measure of toxicity .
2. In patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Anecdotal experience indicates that cerebral edema and cerebral infarction may be caused by Tranexamic Acid Injection in such patients.
3. In patients with active intravascular clotting.
4. In patients with hypersensitivity to tranexamic acid or any of the ingredients
1. In patients with acquired defective color vision, since this prohibits measuring one endpoint that should be followed as a measure of toxicity .
2. In patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Anecdotal experience indicates that cerebral edema and cerebral infarction may be caused by Tranexamic Acid Injection in such patients.
3. In patients with active intravascular clotting.
4. In patients with hypersensitivity to tranexamic acid or any of the ingredients
1. In patients with acquired defective color vision, since this prohibits measuring one endpoint that should be followed as a measure of toxicity .
2. In patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Anecdotal experience indicates that cerebral edema and cerebral infarction may be caused by Tranexamic Acid Injection in such patients.
3. In patients with active intravascular clotting.
4. In patients with hypersensitivity to tranexamic acid or any of the ingredients
1. In patients with acquired defective color vision, since this prohibits measuring one endpoint that should be followed as a measure of toxicity .
2. In patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Anecdotal experience indicates that cerebral edema and cerebral infarction may be caused by Tranexamic Acid Injection in such patients.
3. In patients with active intravascular clotting.
4. In patients with hypersensitivity to tranexamic acid or any of the ingredients
The dose of Tranexamic Acid Injection should be reduced in patients with renal insufficiency because of the risk of accumulation.
Ureteral obstruction due to clot formation in patients with upper urinary tract bleeding has been reported in patients treated with Tranexamic Acid Injection.
Venous and arterial thrombosis or thromboembolism has been reported in patients treated with Tranexamic Acid Injection. In addition, cases of central retinal artery and central retinal vein obstruction have been reported.
Patients with a previous history of thromboembolic disease may be at increased risk for venous or arterial thrombosis.
Tranexamic Acid Injection should not be administered concomitantly with Factor IX Complex concentrates or Anti-inhibitor Coagulant concentrates, as the risk of thrombosis may be increased.
Patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), who require treatment with Tranexamic Acid Injection, must be under strict supervision of a physician experienced in treating this disorder.
Tranexamic acid may cause dizziness and therefore may influence the ability to drive or use machines.
The dose of Tranexamic Acid Injection should be reduced in patients with renal insufficiency because of the risk of accumulation.
Ureteral obstruction due to clot formation in patients with upper urinary tract bleeding has been reported in patients treated with Tranexamic Acid Injection.
Venous and arterial thrombosis or thromboembolism has been reported in patients treated with Tranexamic Acid Injection. In addition, cases of central retinal artery and central retinal vein obstruction have been reported.
Patients with a previous history of thromboembolic disease may be at increased risk for venous or arterial thrombosis.
Tranexamic Acid Injection should not be administered concomitantly with Factor IX Complex concentrates or Anti-inhibitor Coagulant concentrates, as the risk of thrombosis may be increased.
Patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), who require treatment with Tranexamic Acid Injection, must be under strict supervision of a physician experienced in treating this disorder.
Tranexamic acid may cause dizziness and therefore may influence the ability to drive or use machines.
The dose of Tranexamic Acid Injection should be reduced in patients with renal insufficiency because of the risk of accumulation.
Ureteral obstruction due to clot formation in patients with upper urinary tract bleeding has been reported in patients treated with Tranexamic Acid Injection.
Venous and arterial thrombosis or thromboembolism has been reported in patients treated with Tranexamic Acid Injection. In addition, cases of central retinal artery and central retinal vein obstruction have been reported.
Patients with a previous history of thromboembolic disease may be at increased risk for venous or arterial thrombosis.
Tranexamic Acid Injection should not be administered concomitantly with Factor IX Complex concentrates or Anti-inhibitor Coagulant concentrates, as the risk of thrombosis may be increased.
Patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), who require treatment with Tranexamic Acid Injection, must be under strict supervision of a physician experienced in treating this disorder.
Tranexamic acid may cause dizziness and therefore may influence the ability to drive or use machines.
The dose of Tranexamic Acid Injection should be reduced in patients with renal insufficiency because of the risk of accumulation.
Ureteral obstruction due to clot formation in patients with upper urinary tract bleeding has been reported in patients treated with Tranexamic Acid Injection.
Venous and arterial thrombosis or thromboembolism has been reported in patients treated with Tranexamic Acid Injection. In addition, cases of central retinal artery and central retinal vein obstruction have been reported.
Patients with a previous history of thromboembolic disease may be at increased risk for venous or arterial thrombosis.
Tranexamic Acid Injection should not be administered concomitantly with Factor IX Complex concentrates or Anti-inhibitor Coagulant concentrates, as the risk of thrombosis may be increased.
Patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), who require treatment with Tranexamic Acid Injection, must be under strict supervision of a physician experienced in treating this disorder.
Tranexamic acid may cause dizziness and therefore may influence the ability to drive or use machines.
The dose of Tranexamic Acid Injection should be reduced in patients with renal insufficiency because of the risk of accumulation.
Ureteral obstruction due to clot formation in patients with upper urinary tract bleeding has been reported in patients treated with Tranexamic Acid Injection.
Venous and arterial thrombosis or thromboembolism has been reported in patients treated with Tranexamic Acid Injection. In addition, cases of central retinal artery and central retinal vein obstruction have been reported.
Patients with a previous history of thromboembolic disease may be at increased risk for venous or arterial thrombosis.
Tranexamic Acid Injection should not be administered concomitantly with Factor IX Complex concentrates or Anti-inhibitor Coagulant concentrates, as the risk of thrombosis may be increased.
Patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), who require treatment with Tranexamic Acid Injection, must be under strict supervision of a physician experienced in treating this disorder.
Tranexamic acid may cause dizziness and therefore may influence the ability to drive or use machines.
No studies of interaction between tranexamic acid and other drugs have been conducted.
[#delta] => 0 ) [#title] => [#description] => [#theme_used] => 1 [#printed] => 1 [#type] => [#value] => [#prefix] => [#suffix] => [#children] =>No studies of interaction between tranexamic acid and other drugs have been conducted.
) [#title] => [#description] => [#children] =>No studies of interaction between tranexamic acid and other drugs have been conducted.
[#printed] => 1 ) [#single] => 1 [#attributes] => Array ( ) [#required] => [#parents] => Array ( ) [#tree] => [#context] => full [#page] => 1 [#field_name] => field_drug_interactions [#title] => Drug Interactions [#access] => 1 [#label_display] => above [#teaser] => [#node] => stdClass Object *RECURSION* [#type] => content_field [#children] =>No studies of interaction between tranexamic acid and other drugs have been conducted.
[#printed] => 1 ) [#title] => [#description] => [#children] =>No studies of interaction between tranexamic acid and other drugs have been conducted.
Back pain; headache; joint pain; muscle pain, spasms, or cramps; nasal or sinus congestion; stomach pain; tiredness.
Severe allergic reactions (rash; hives; itching; difficulty breathing; tightness in the chest or throat; swelling of the mouth, face, lips, or tongue; flushing of the face); calf or leg pain, swelling, or tenderness; chest pain; confusion; coughing up blood; decreased urination or difficulty urinating; eye problems; fainting; numbness of an arm or leg; one-sided weakness; seizures; severe or persistent dizziness or light-headedness; shortness of breath; slurred speech; sudden, severe headache or vomiting; unusual tiredness or weakness; vision changes or problems (eg, disturbance of color vision, sharpness, or field of vision).
Back pain; headache; joint pain; muscle pain, spasms, or cramps; nasal or sinus congestion; stomach pain; tiredness.
Severe allergic reactions (rash; hives; itching; difficulty breathing; tightness in the chest or throat; swelling of the mouth, face, lips, or tongue; flushing of the face); calf or leg pain, swelling, or tenderness; chest pain; confusion; coughing up blood; decreased urination or difficulty urinating; eye problems; fainting; numbness of an arm or leg; one-sided weakness; seizures; severe or persistent dizziness or light-headedness; shortness of breath; slurred speech; sudden, severe headache or vomiting; unusual tiredness or weakness; vision changes or problems (eg, disturbance of color vision, sharpness, or field of vision).
Back pain; headache; joint pain; muscle pain, spasms, or cramps; nasal or sinus congestion; stomach pain; tiredness.
Severe allergic reactions (rash; hives; itching; difficulty breathing; tightness in the chest or throat; swelling of the mouth, face, lips, or tongue; flushing of the face); calf or leg pain, swelling, or tenderness; chest pain; confusion; coughing up blood; decreased urination or difficulty urinating; eye problems; fainting; numbness of an arm or leg; one-sided weakness; seizures; severe or persistent dizziness or light-headedness; shortness of breath; slurred speech; sudden, severe headache or vomiting; unusual tiredness or weakness; vision changes or problems (eg, disturbance of color vision, sharpness, or field of vision).
Back pain; headache; joint pain; muscle pain, spasms, or cramps; nasal or sinus congestion; stomach pain; tiredness.
Severe allergic reactions (rash; hives; itching; difficulty breathing; tightness in the chest or throat; swelling of the mouth, face, lips, or tongue; flushing of the face); calf or leg pain, swelling, or tenderness; chest pain; confusion; coughing up blood; decreased urination or difficulty urinating; eye problems; fainting; numbness of an arm or leg; one-sided weakness; seizures; severe or persistent dizziness or light-headedness; shortness of breath; slurred speech; sudden, severe headache or vomiting; unusual tiredness or weakness; vision changes or problems (eg, disturbance of color vision, sharpness, or field of vision).
Back pain; headache; joint pain; muscle pain, spasms, or cramps; nasal or sinus congestion; stomach pain; tiredness.
Severe allergic reactions (rash; hives; itching; difficulty breathing; tightness in the chest or throat; swelling of the mouth, face, lips, or tongue; flushing of the face); calf or leg pain, swelling, or tenderness; chest pain; confusion; coughing up blood; decreased urination or difficulty urinating; eye problems; fainting; numbness of an arm or leg; one-sided weakness; seizures; severe or persistent dizziness or light-headedness; shortness of breath; slurred speech; sudden, severe headache or vomiting; unusual tiredness or weakness; vision changes or problems (eg, disturbance of color vision, sharpness, or field of vision).
• Store below 30 C°
• Protect from light and freezing
• Store below 30 C°
• Protect from light and freezing
• Store below 30 C°
• Protect from light and freezing
• Store below 30 C°
• Protect from light and freezing
• Store below 30 C°
• Protect from light and freezing
• Injection 500mg/5ml: Box of 5 ampoules
[#delta] => 0 ) [#title] => [#description] => [#theme_used] => 1 [#printed] => 1 [#type] => [#value] => [#prefix] => [#suffix] => [#children] =>• Injection 500mg/5ml: Box of 5 ampoules
) [#title] => [#description] => [#children] =>• Injection 500mg/5ml: Box of 5 ampoules
[#printed] => 1 ) [#single] => 1 [#attributes] => Array ( ) [#required] => [#parents] => Array ( ) [#tree] => [#context] => full [#page] => 1 [#field_name] => field_packing [#title] => Packing [#access] => 1 [#label_display] => above [#teaser] => [#node] => stdClass Object *RECURSION* [#type] => content_field [#children] =>• Injection 500mg/5ml: Box of 5 ampoules
[#printed] => 1 ) [#title] => [#description] => [#children] =>• Injection 500mg/5ml: Box of 5 ampoules

TRANEXIP®
Injection 500mg/5ml
Antifibrinolytic Agent
Haemostatics
Category B
Tranexamic acid is a competitive inhibitor of plasminogen activation, and at much higher concentrations, a noncompetitive inhibitor of plasmin, i.e., actions similar to aminocaproic acid. Tranexamic acid is about 10 times more potent in vitro than aminocaproic acid.
Tranexamic acid binds more strongly than aminocaproic acid to both the strong and weak receptor sites of the plasminogen molecule in a ratio corresponding to the difference in potency between the compounds. Tranexamic acid in a concentration of 1 mg per mL does not aggregate platelets in vitro.
Tranexamic acid in concentrations up to 10 mg per mL blood has no influence on the platelet count, the coagulation time, or various coagulation factors in whole blood or citrated blood from normal subjects. On the other hand, tranexamic acid in concentrations of 10 mg and 1 mg per mL blood prolongs the thrombin time.
The plasma protein binding of tranexamic acid is about 3% at therapeutic plasma levels and seems to be fully accounted for by its binding to plasminogen. Tranexamic acid does not bind to serum albumin.
After an intravenous dose of 1 g, the plasma concentration time curve shows a triexponential decay with a half-life of about 2 hours for the terminal elimination phase. The initial volume of distribution is about 9 to 12 liters. Urinary excretion is the main route of elimination via glomerular filtration. Overall renal clearance is equal to overall plasma clearance (110 to 116 mL/min), and more than 95% of the dose is excreted in the urine as the unchanged drug. Excretion of tranexamic acid is about 90% at 24 hours after intravenous administration of 10 mg per kg body weight.
An antifibrinolytic concentration of tranexamic acid remains in different tissues for about 17 hours, and in the serum, up to seven or eight hours.
Tranexamic acid passes through the placenta. The concentration in cord blood after an intravenous injection of 10 mg per kg to pregnant women is about 30 mg per liter, as high as in the maternal blood. Tranexamic acid diffuses rapidly into joint fluid and the synovial membrane. In the joint fluid, the same concentration is obtained as in the serum. The biological half-life of tranexamic acid in the joint fluid is about three hours.
The concentration of tranexamic acid in a number of other tissues is lower than in blood. In breast milk, the concentration is about one hundredth of the serum peak concentration. Tranexamic acid concentration in cerebrospinal fluid is about one tenth of that of the plasma. The drug passes into the aqueous humor, the concentration being about one tenth of the plasma concentration.
Tranexamic acid has been detected in semen where it inhibits fibrinolytic activity but does not influence sperm migration.
-
Tranexamic Acid Injection is indicated in patients with hemophilia for short-term use (two to eight days) to reduce or prevent hemorrhage and reduce the need for replacement therapy during and following tooth extraction.
1. In patients with acquired defective color vision, since this prohibits measuring one endpoint that should be followed as a measure of toxicity .
2. In patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Anecdotal experience indicates that cerebral edema and cerebral infarction may be caused by Tranexamic Acid Injection in such patients.
3. In patients with active intravascular clotting.
4. In patients with hypersensitivity to tranexamic acid or any of the ingredients
The dose of Tranexamic Acid Injection should be reduced in patients with renal insufficiency because of the risk of accumulation.
Ureteral obstruction due to clot formation in patients with upper urinary tract bleeding has been reported in patients treated with Tranexamic Acid Injection.
Venous and arterial thrombosis or thromboembolism has been reported in patients treated with Tranexamic Acid Injection. In addition, cases of central retinal artery and central retinal vein obstruction have been reported.
Patients with a previous history of thromboembolic disease may be at increased risk for venous or arterial thrombosis.
Tranexamic Acid Injection should not be administered concomitantly with Factor IX Complex concentrates or Anti-inhibitor Coagulant concentrates, as the risk of thrombosis may be increased.
Patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), who require treatment with Tranexamic Acid Injection, must be under strict supervision of a physician experienced in treating this disorder.
Tranexamic acid may cause dizziness and therefore may influence the ability to drive or use machines.
No studies of interaction between tranexamic acid and other drugs have been conducted.
Back pain; headache; joint pain; muscle pain, spasms, or cramps; nasal or sinus congestion; stomach pain; tiredness.
Severe allergic reactions (rash; hives; itching; difficulty breathing; tightness in the chest or throat; swelling of the mouth, face, lips, or tongue; flushing of the face); calf or leg pain, swelling, or tenderness; chest pain; confusion; coughing up blood; decreased urination or difficulty urinating; eye problems; fainting; numbness of an arm or leg; one-sided weakness; seizures; severe or persistent dizziness or light-headedness; shortness of breath; slurred speech; sudden, severe headache or vomiting; unusual tiredness or weakness; vision changes or problems (eg, disturbance of color vision, sharpness, or field of vision).
• Store below 30 C°
• Protect from light and freezing
• Injection 500mg/5ml: Box of 5 ampoules